
TSC released a toolkit of products in the coffee category into the public domain. In doing so, it hopes to encourage commercial and nonprofit organizations throughout the coffee supply chain to meet the growing demand for coffee in a smart, sustainable way.
One tool in TSC’s toolkit is the hot spot diagram, showing activity within coffee’s lifecycle that is identified as having a substantial environmental or social impact that is supported by significant evidence. The hot spots in coffee production include deforestation and biodiversity loss caused by land transformation, labor and human rights issues such as child or forced labor, and impacts to resource stocks such as ground and surface water depletion caused by irrigation water use in water-scarce areas.

The Sustainability Consortium, 2019
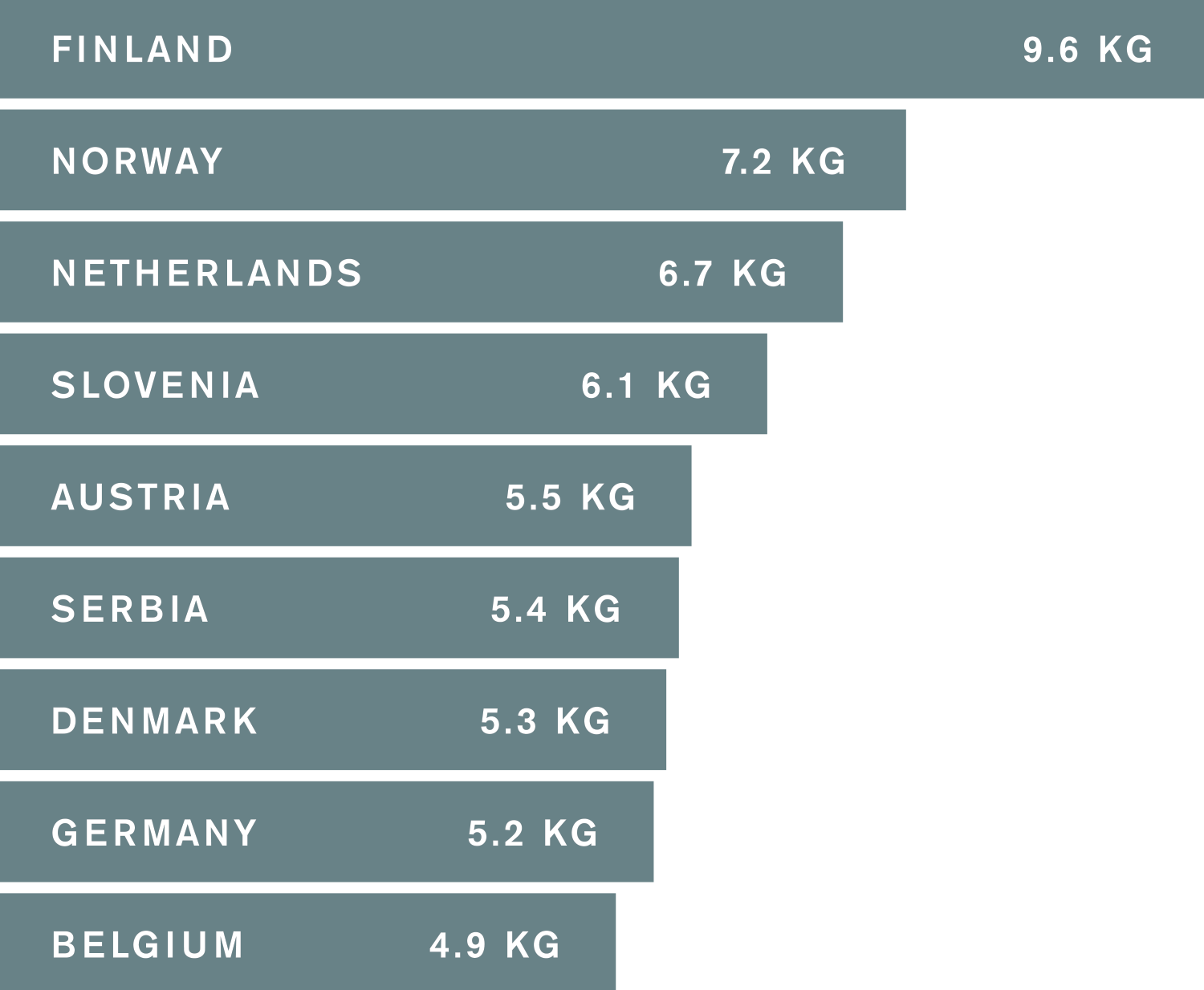
(per person on average)



To address this, the Sustainable Coffee Challenge was formed “to make coffee the first sustainable agricultural product in the world.” The Sustainability Consortium (TSC), which is jointly administered by Arizona State University and the University of Arkansas, is a proud member of the Sustainable Coffee Challenge that is led by one of TSC’s key partners, Conservation International.
TSC released a toolkit of products in the coffee category into the public domain. In doing so, it hopes to encourage commercial and nonprofit organizations throughout the coffee supply chain to meet the growing demand for coffee in a smart, sustainable way.
One tool in TSC’s toolkit is the hot spot diagram, showing activity within coffee’s lifecycle that is identified as having a substantial environmental or social impact that is supported by significant evidence. The hot spots in coffee production include deforestation and biodiversity loss caused by land transformation, labor and human rights issues such as child or forced labor, and impacts to resource stocks such as ground and surface water depletion caused by irrigation water use in water-scarce areas.

The Sustainability Consortium, 2019
(per person on average)



572,000 miles farm to U.S.
(thousands of metric tons)
United States: 971
Brazil: 969
Germany: 425
Italy: 211
France: 202
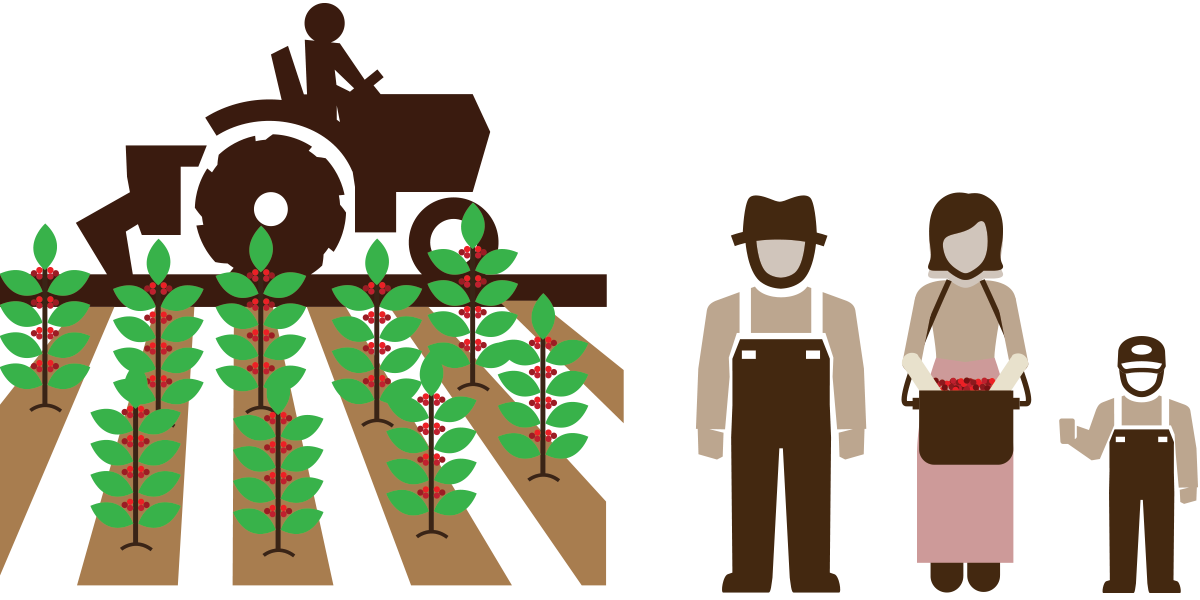
Child labor use (on farm): Issues involved in child labor use in coffee farming may include no pay, long working hours, dangerous working conditions, and limited access to education.
Energy consumption (on farm): Fuel combustion and energy generated to power farm operations can cause climate change, deplete resources, and affect human health.
Fertilizer application (on farm): Fertilizer use can affect soil and water quality and cause climate change.
Labor rights (on farm): Farm workers are at risk of several labor rights issues such as unfair pay, discrimination, and sexual harassment and assault.
Land transformation (on farm): The conversion of forest to coffee farms can lead to environmental impacts and climate change from deforestation.
Supply chain traceability: Due to the complexity of coffee supply chains, information about where the supply chain originates is limited, which is a challenge to improving issues.
Water use (on farm): Using water for irrigation can deplete freshwater resources and lead to poor soil quality.
Worker health and safety (on farm): Farm workers can develop serious health problems from exposure to chemicals, noise, and dust and physical injury from other occupational hazards.













Get TSC’s other tools in its toolkit, including improvement opportunities in the coffee supply chain, KPIs to measure and share progress around key issues, and research reports as a basis for raising awareness and focusing action: